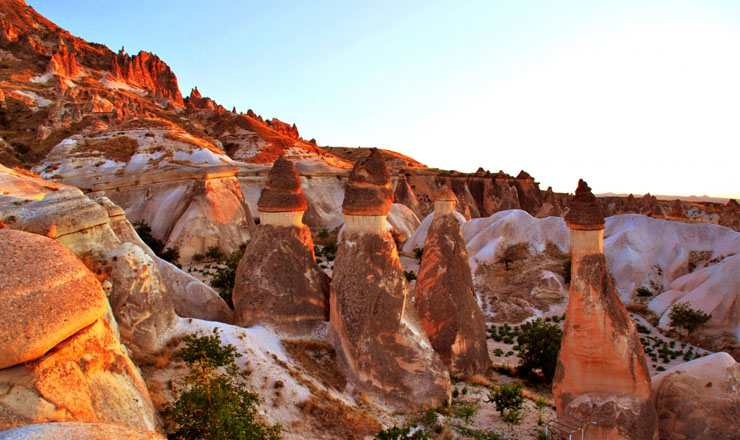


Cappadocia region was formed 60 million years ago by erosion of soft layers of lava and ash from Mount Erciyes (Argeus), Mount Hasan and Mount Güllü composing with wind and rain over millions of years.
Human settlement at the Cappadocia region dates back to the Paleolithic era. The lands where the Hittites once lived have been one of the most important centers of Christianity in the later periods. Houses and churches carved into the caves and rocks turned the region into a huge heaven for Christians escaping from the dominance of the Roman Empire.
Cappadocia is a region spreading an area covering the provinces particularly to Nevsehir, Kirsehir, Nigde, Aksaray and Kayseri.
The region of Cappadocia is a place where nature and history integrates. While geographical events created fairy chimneys – the people carved houses and churches inside these chimneys. Later on decorated them with frescoes in this historical process, bringing the traces of civilizations for thousands of years to present. Written history of Cappadocia, where human settlement dates back to the Paleolithic era, begins with the Hittites. Hosting trade colonies throughout history and founding commercial and social bridges between countries, Cappadocia was one of the important junctions of the Silk Road.
In the 12th century BC, a dark period began in the region with the collapse of the Hittite Empire. During this period, the late Hittite Kings with effects of Assyria and Phrygia ruled the region. These Kingdoms lasted until the Persian invasion in the 6th century BC. The word used today, Cappadocia, means "Land of Beautiful Horses" in Persian. In 332 BC, Alexander the Great defeated the Persians and encountered great resistance in Cappadocia. During this period, the Kingdom of Cappadocia was established. The Roman power began to be felt in the region towards the end of the 3rd century BC. In the middle of 1st century, Kings of Cappadocia were appointed and toppled from the throne by the Roman Generals. When the last king of Cappadocia died in 17 AD, the region became a province of Rome.
In the 3rd century, Christians came to the Cappadocia which became a centre for education. Pressure on the Christians increased between 303-308. But Cappadocia was an ideal place to be safeguarded from pressures and to spread the Christian doctrine. Deep valleys and shelters dug into the soft volcanic rocks created a safe heaven against the Roman soldiers.
The 4th century is the period of the people known as "Fathers of Cappadocia." But the importance of the region reached its climax when Leon III, Emperor of Rome banned icons. Under these circumstances, some people who were pro-icon started to take shelter in the region. Iconoclasm movement lasted more than a hundred years (726-843). Although some Cappadocian churches were under the influence of Iconoclasm in this period, pro-icon people easily continued worshipping here. The monasteries of Cappadocia developed considerably during this period.
Again, in these periods, Arab raids started to affect the Christian regions in Anatolia, from Armenia to Cappadocia. People escaping the invasion and coming to the region changed the styles of churches in the area. In 11th and 12th centuries Cappadocia passed into the hands of the Seljuk Turks. The region spent a period without trouble subsequent times under the Ottoman Empire. The last Christians in the region migrated from Cappadocia due to the exchange of Treaty of Lausanne in 1924-26, leaving beautiful architectural examples behind.